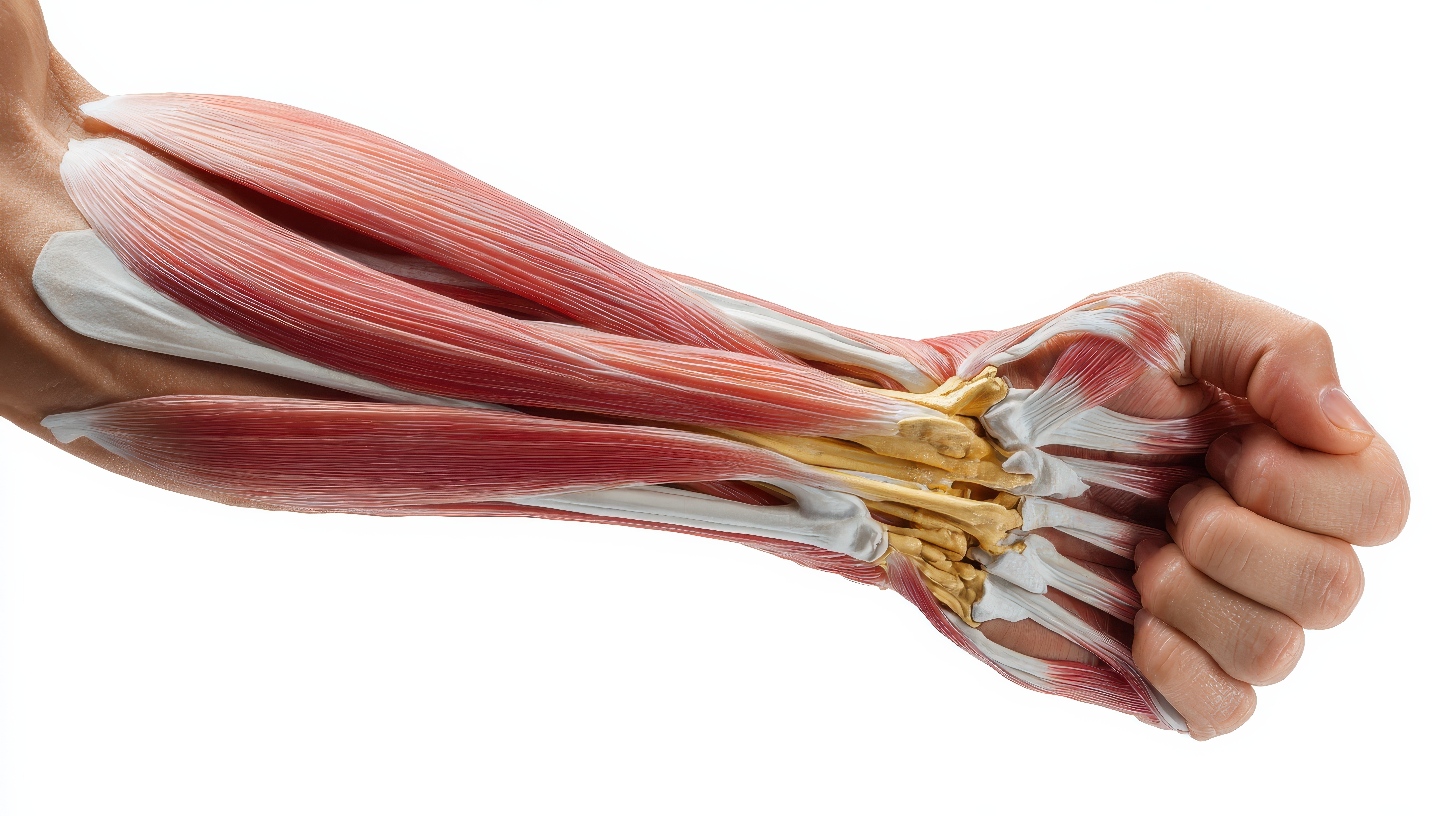
Anatomy & Function
What Are Muscles?
Muscles are soft tissues made up of fibres that contract and relax to produce movement. They work with your bones and joints to help you sit, stand, walk, and perform daily activities. The body has three main types of muscles:
Skeletal muscles attached to bones, control voluntary movement
Smooth muscles found in organs, control involuntary functions like digestion
Cardiac muscle found only in the heart
Skeletal muscles make up the majority of muscle mass and are directly linked to strength, balance, posture, and physical performance.
Physiological Significance
Why Do They Matter?
Muscles do more than power our movements — they play a vital role in recovery, stamina, and long-term health. When muscles are strong, the body functions better across all stages of life.
Faster Recovery
Aids healing after illness, injury, or surgery.
Mobility & Independence
Keeps you moving freely and living independently as you age.
Boosted Endurance
Supports energy use and overall physical stamina.
Reduced Health Risks
Lowers the risk of falls, fatigue, and physical decline.
Understanding Muscle Systems
Key Concepts About Muscles
Muscle Biology
Understand how muscles work, adapt, and support everyday movement

Muscle Weakness Overview
Learn about early signs of muscle loss and why it’s often overlooked

Complications
Explore how untreated muscle weakness can impact recovery, balance, and quality of life
Disease-Associated Factors
Understand how chronic conditions like diabetes and arthritis can worsen muscle health

Non-Disease Factors
Discover lifestyle and age-related factors that lead to muscle decline




